products
Bone Metabolism
Cancer Markers
Cardiac Markers
Diabetes
Endocrinology
Gastroenterology
Hormones
Immunology
services
Assay Validation and Verification studies
Immunoassay Development
Drug discovery through cutting edge technology in automation like LC-MS/MS
Developing Point of care instrument and Micro fluidic cartridge
Latest News
Hormones
A hormone (from Greek á½Ïμή, "impetus") is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Hormones in animals are often transported in the blood. Cells respond to a hormone when they express a specific receptor for that hormone. Endocrine hormone molecules are secreted (released) directly into the bloodstream.
Hormone cells are typically of a specialized cell type, residing within a particular endocrine gland, such as thyroid gland, ovaries, and testes. Cellular recipients of a particular hormonal signal may be one of several cell types that reside within a number of different tissues, as is the case for insulin, which triggers a diverse range of systemic physiological effects.
For hormones such as steroid or thyroid hormones, their receptors are located intracellularly within the cytoplasm of their target cell. The combined hormone-receptor complex then moves across the nuclear membrane into the nucleus of the cell, where it binds to specific DNA sequences, effectively amplifying or suppressing the action of certain genes, and affecting protein synthesis.
Vertebrate hormones fall into three chemical classes:
Peptide hormones consist of chains of amino acids. Examples of small peptide hormones are TRH and vasopressin. Peptides composed of scores or hundreds of amino acids are referred to as proteins. Examples of protein hormones include insulin and growth hormone. More complex protein hormones bear carbohydrate side-chains and are called glycoprotein hormones. Luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone and thyroid-stimulating hormone are glycoprotein hormones.
Lipid and phospholipid-derived hormones derive from lipids such as linoleic acid and arachidonic acid and phospholipids. The main classes are the steroid hormones that derive from cholesterol and the eicosanoids. Examples of steroid hormones are testosterone and cortisol. The adrenal cortex and the gonads are primary sources of steroid hormones.
Monoamines derived from aromatic amino acids like phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan by the action of aromatic amino acid decarboxylase enzymes.
Life Biological ELISA kits detect the hormones with 99.5 percent specificity and very high sensitivity.
LH
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) ELISA
Specification:
Catalog Number: LH HU-LB27
Description: Luteinizing Hormone ELISA
Sample Type:...
find more
Human Chorionic Gonadtropin
hCG ELISA
Specification:
Catalog Number: hCG HU-LB29
Description: hCG ELISA
Sample Type: Serum
Sample Size: 10 µ...
find more
FSH ELISA
FSH ELISA
Specification:
Catalog Number: FSH HU-LB28
Description: FSH ELISA
Sample Type: Serum
Sample Size: 5...
find more
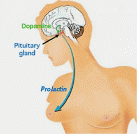
Prolactin ELISA
Prolactin ELISA
Specification:
Catalog Number: PRL HU-LB25
Description: Prolactin ELISA
Sample Type: Serum
Sa...
find more